Kubernetes¶
Now you can operate Kubernetes cluster from Nurtch notebooks. You can either use the familiar kubectl commands or use higher level APIs provided by Rubix library.
Setup¶
Once you login, go to the admin tab and upload Kubernetes config file. The file is typically located at ~/.kube/config. Tip: You might need to press (CMD + Shift + .) on mac to show hidden files in the finder.
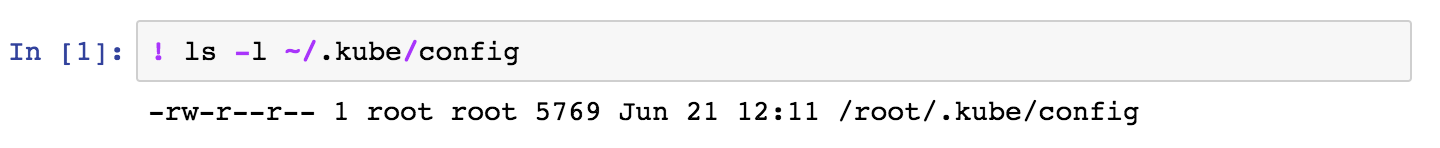
Once uploaded, wait for a minute for the config to propagate to all the nodes in your cluster. You can verify if the config is propagated as shown below.
That’s it! Now you can use kubectl commands and rubix.kubernetes.* methods to operate your cluster (examples below).
Command Line Usage¶
You can upload and use your existing scripts in the notebook or use one-off commands as shown in the examples below.
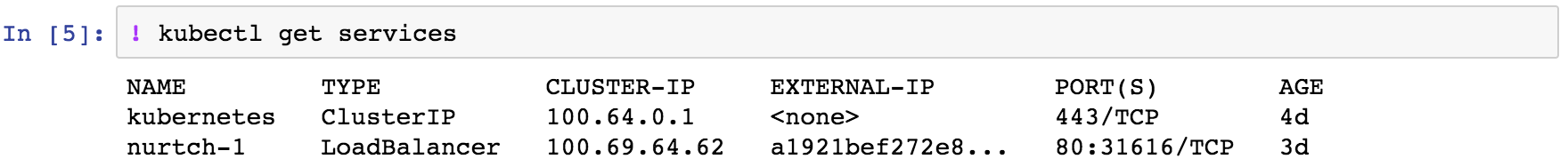
- List all running services.
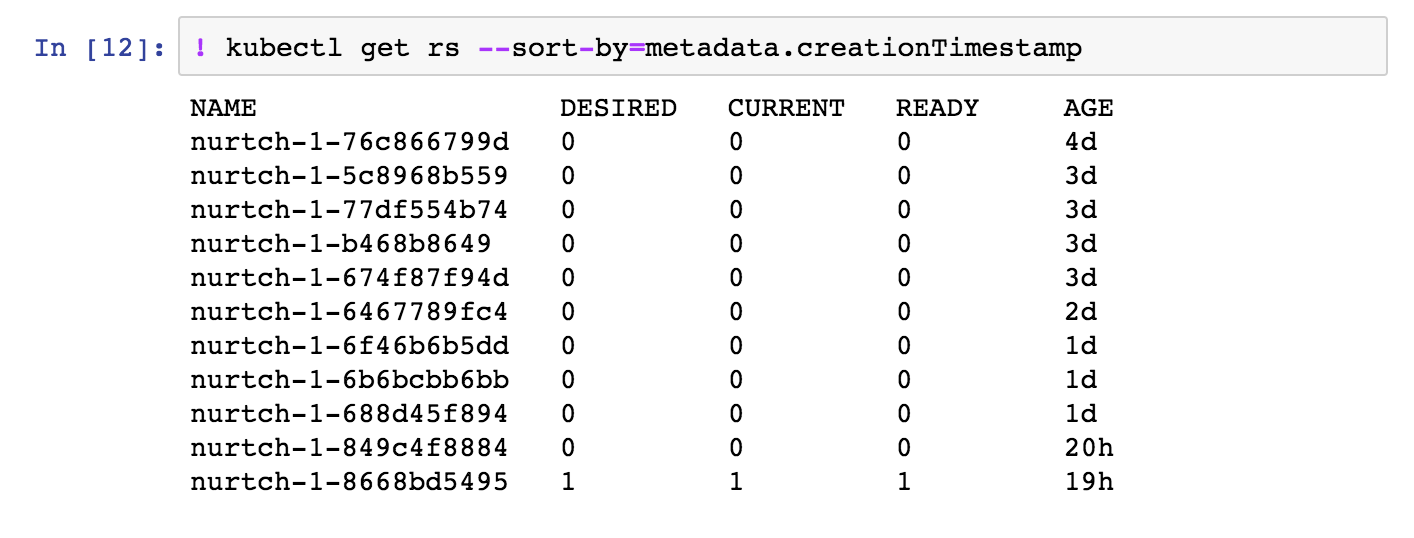
- See when deployments occurred in your cluster by checking replica sets.
- See the rollout history with kubectl rollout history <resource_name> and rollback to the version you wish.

- Check the status of your deployment rollout.

API Usage¶
-
get_latest_deployment_status(service_name, namespace='default', context=None)¶ Retrieve metadata of last deployment on your Kubernetes service. Metadata includes deployment time, desired/available/current counts, container image etc.
Parameters: - service (
str) – Name of your Kubernetes service. - namespace (
str) – Namespace under which your service is running, if using namespaces. - context – Context under which your service is running, if using context. Since context specifies the trio of (cluster, user, namespace) you don’t need to specify namespace separately while using context.
Returns: dict – See response section below.
Response: - desiredCount (
int) - The desired number of replicas of the application.
- desiredCount (
- availableCount (
int) - The number of replicas that are available to your users.
- availableCount (
- currentCount (
int) - The number of replicas that are currently running.
- currentCount (
- createdAt (
datetime.datetime) - The Unix time stamp for when the deployment was created.
- createdAt (
- containerImage (
str) - The name of container image + tag that got deployed.
- containerImage (
Examples: from rubix.kubernetes import get_latest_deployment_status get_latest_deployment_status(service_name='nurtch-1')
Sample Usage and Output: 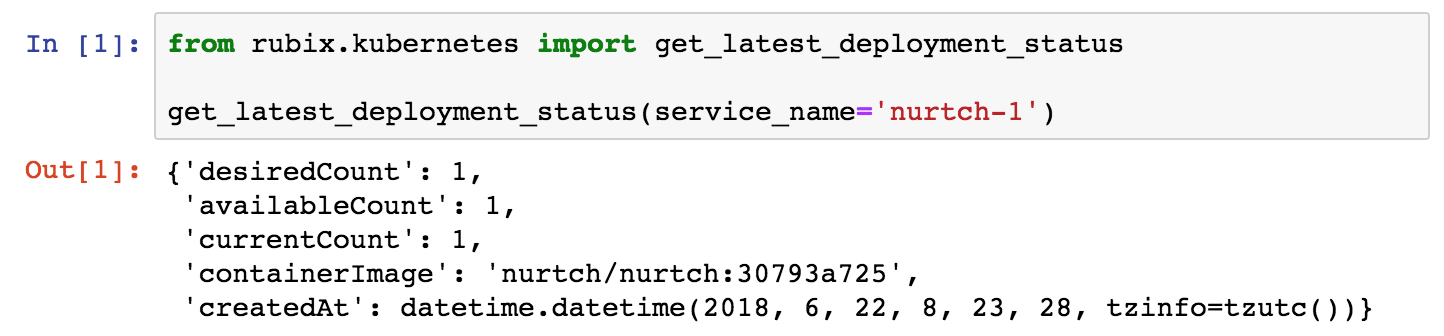
- service (